Many manufacturers struggle when producing parts with complex shapes using standard 3-axis CNC machines. This often results in time-consuming setups and inconsistent quality.
4-axis CNC machines add a rotating motion to the standard three axes, allowing for advanced machining on multiple surfaces in a single setup.
This technology reduces production time, increases accuracy, and opens the door to more complex designs that are not possible with basic CNC machines.
How does 4-axis motion work?
Simple machining tools can only cut in straight lines or basic curves. But what if the design requires angled holes or circular cuts around a cylinder?
4-axis motion works by adding a rotational axis to the traditional X, Y, and Z movements, allowing the machine to turn the part during cutting.

In most CNC machines, the cutting tool moves in three directions: side-to-side (X), front-to-back (Y), and up-and-down (Z). A 4-axis CNC adds a fourth movement: rotation around the X-axis, called the A-axis. This allows the workpiece to rotate while the tool moves, cutting all sides without stopping.
Motion Breakdown Table
| Axis | Movement | Description |
|---|---|---|
| X | Left to right | Horizontal movement |
| Y | Front to back | Vertical movement |
| Z | Up and down | Tool height and depth |
| A | Around the X-axis | Rotates the part while machining |
This extra motion makes a big difference when working with parts that have holes or patterns on different faces. It also reduces the need to reposition the part manually, which can introduce mistakes.
Advantages of the A-axis
- Cuts on multiple sides without manual re-clamping
- Increases precision by keeping parts aligned
- Saves time with fewer setups
By rotating the part during the machining process, 4-axis CNC machines help ensure higher accuracy and consistent results across every piece.
Why choose 4-axis machining?
Many production lines lose time and precision due to frequent part repositioning. This adds errors and increases costs.
4-axis machining reduces human error, improves efficiency, and ensures consistency in producing complex parts with fewer setups.
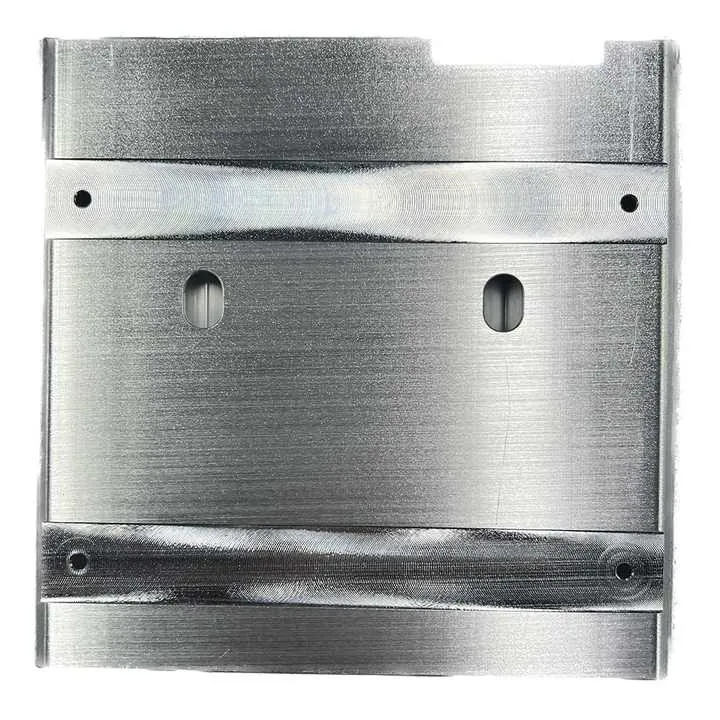

When using only 3-axis machines, workers must stop the process and reposition the part to cut different sides. This takes time and can lead to slight misalignments. 4-axis CNC machines avoid this by rotating the part automatically.
Workflow Comparison Table
| Process Step | 3-Axis CNC | 4-Axis CNC |
|---|---|---|
| Number of setups | Multiple | Usually one |
| Risk of misalignment | High | Very low |
| Operator time | Long | Shorter |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Part consistency | Variable | High repeatability |
This kind of efficiency makes a real difference in industries where precision and speed are critical.
Industries That Benefit
- Aerospace companies that need consistent accuracy
- Automotive manufacturers producing engine parts
- Medical suppliers working with small, detailed items
By reducing time, cost, and waste, 4-axis CNC machining helps businesses stay competitive and meet high-quality standards.
Which parts require 4-axis?
Some parts are too complex for basic 3-axis machines. They need cutting from multiple sides or at unusual angles.
Parts with curves, angled holes, or features on more than one face are best made using 4-axis CNC machines.
These machines are especially useful for parts that must be machined from all directions without stopping the process. That includes everything from small custom brackets to large frames.
Examples of Common Parts
| Part Type | Reason for 4-Axis Machining |
|---|---|
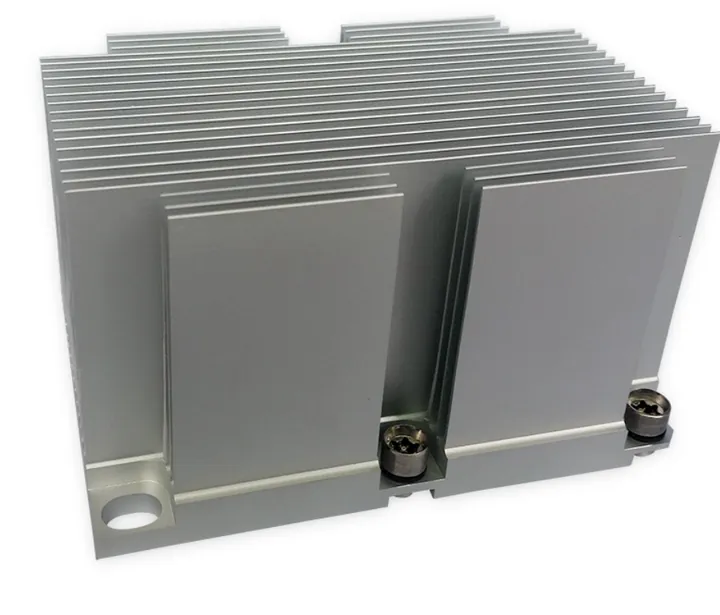
| Cylindrical housings | Require hole drilling around the sides |
| Turbine blades | Need curved surface machining |
| Fixture bases | Have angled mounting holes |
| Enclosure panels | Machined on multiple faces in one cycle |
Custom Aluminum Brackets
These are often used in machinery and electronics. Many of them need cuts on opposite sides or even wrap-around engravings. Instead of flipping the part manually, the machine rotates it and finishes the job in one go.
Solar Panel Mounting Frames
Some solar panel brackets have slots and holes at specific angles to hold the panel securely. These designs benefit from 4-axis CNC because the machine keeps every angle accurate without stopping to reset the part.
By using this method, manufacturers can deliver consistent quality across hundreds or thousands of units with less downtime and fewer mistakes.
Where is 4-axis CNC used?
Many people think this technology is only used in aerospace, but it is now common in many other industries.
4-axis CNC machining is widely used in automotive, electronics, medical, energy, and custom manufacturing applications.
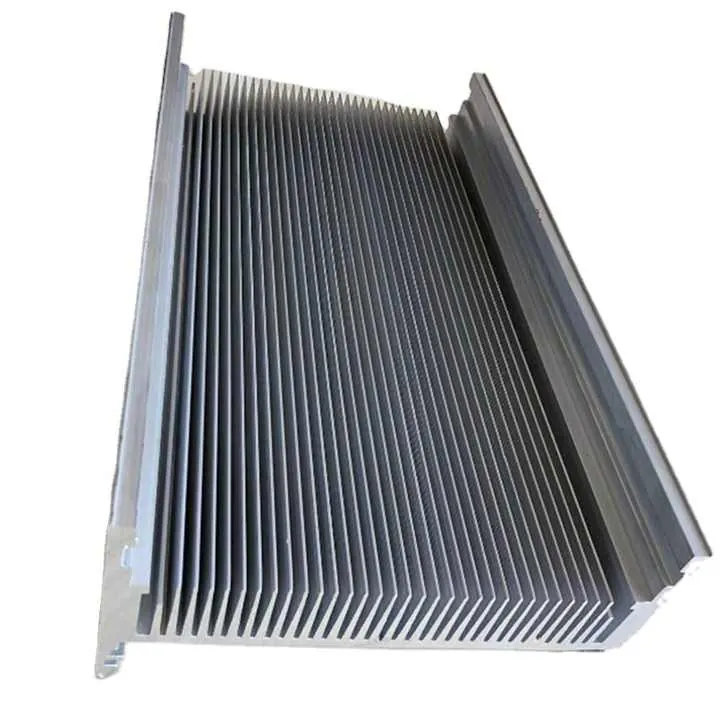

As part designs become more complex, more industries are turning to 4-axis CNC machining to stay competitive and meet tight production timelines.
Applications Across Industries
| Industry | Application Examples |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Transmission housings, steering components |
| Aerospace | Wing connectors, curved brackets |
| Medical | Implants, precision instruments |
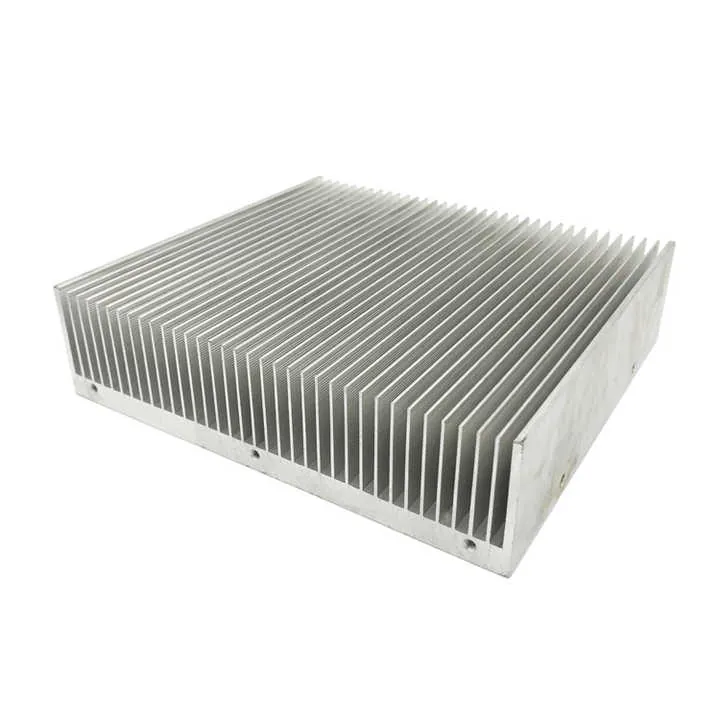
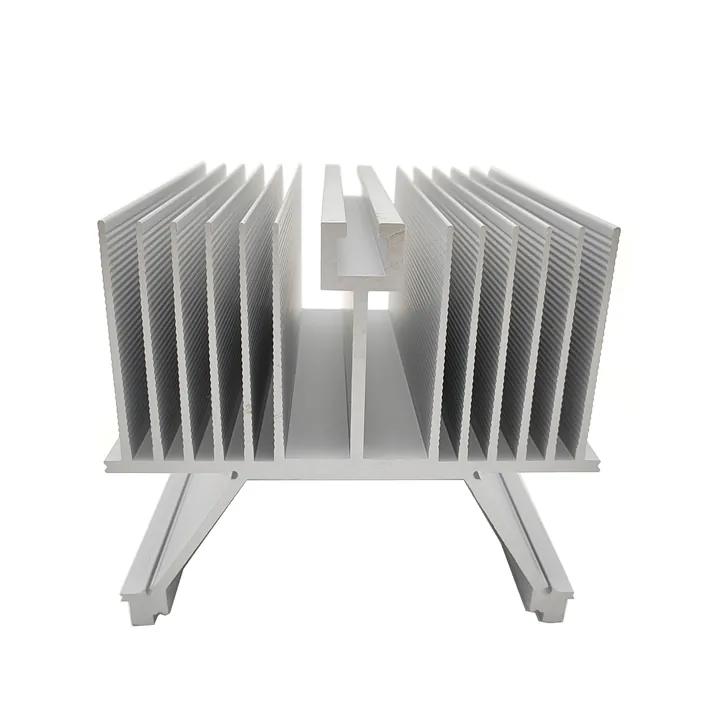
| Electronics | Heat sinks, sensor housings |
| Energy | Wind turbine brackets, panel frames |
Focus on Aluminum
Aluminum is one of the most popular materials used in 4-axis CNC machining because it is lightweight, strong, and easy to cut.
Many of the parts we supply to clients in Europe and North America include:
- Precision-cut LED housing frames
- Mounting plates with side features
- Custom CNC heat dissipation covers
These items often have slots, mounting holes, and other features on several sides, making them ideal candidates for 4-axis production. Clients benefit from fast lead times, tight tolerances, and consistent results.
Whether it's a simple support bracket or a complex panel with cutouts and logos, 4-axis CNC machining keeps everything aligned and accurate.
Conclusion
4-axis CNC machining improves speed, accuracy, and consistency. It is perfect for complex shapes, multi-sided parts, and industries that demand precision without compromise.






