Modern production demands faster, more precise, and repeatable results. Relying only on manual machining often leads to inconsistent quality, wasted materials, and longer production times.
CNC machining provides superior efficiency, accuracy, and scalability compared to manual processes. It minimizes human error, reduces waste, and allows for complex shapes with consistent quality.
If you're wondering whether to invest in CNC machining, this article will help you understand how it outperforms manual methods in key areas.
How does CNC machining improve efficiency?
When every second counts in a production line, manual methods can slow things down. Operators need rest, can make errors, and often need to recalibrate or reposition materials.
CNC machining improves efficiency by automating complex tasks, reducing cycle times, and enabling 24/7 operation with minimal supervision.

Continuous operation with fewer interruptions
CNC machines can run day and night without breaks. A well-programmed CNC setup can complete dozens of parts in a single cycle, without stopping between operations. Manual machines, by contrast, rely on the operator's pace and skill.
Multi-axis capabilities
Unlike manual lathes or mills, CNC machines with 3, 4, or 5 axes can handle complex geometries in one setup. This saves hours of retooling or repositioning required in manual processes.
| Feature | CNC Machining | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Hours | 24/7 with supervision | Limited by labor |
| Setup Time | One-time program load | Frequent retooling |
| Output Speed | Fast and consistent | Slower and variable |
| Labor Requirement | Minimal once set | Constant monitoring |
Reduced material waste
Because CNC machines follow exact digital instructions, there's less risk of human error. This reduces material waste and the need for rework, which can save thousands over time.
In short, CNC machining helps factories meet tighter deadlines, reduce labor costs, and improve throughput without sacrificing quality.
Why is CNC machining more precise than manual methods?
Even the best machinist cannot match the repeatability and consistency of a machine controlled by computer instructions.
CNC machining achieves higher precision by following exact digital instructions, eliminating human error and ensuring consistent quality across all parts.
Tolerances matter
CNC machines operate within extremely tight tolerances, often as low as ±0.002 mm. Manual machining rarely reaches this level, especially over multiple parts.
No variation from fatigue
Manual work depends on the operator’s focus, which can vary. Fatigue, distraction, or even a small misalignment can ruin a part. CNC machines, once set up, deliver the same result every time.
| Precision Factor | CNC Machining | Manual Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Tolerance | ±0.002 mm | ±0.05 mm |
| Repeatability | Excellent | Inconsistent |
| Human Error | Eliminated | High |
| Part Consistency (Batch) | Uniform | Variable |
Consistency across batches
When producing hundreds or thousands of parts, consistency becomes critical. CNC machining guarantees that part number 1 and part number 1,000 are indistinguishable, something manual processes cannot assure.
If a part needs to fit precisely into an assembly, even a small deviation can cause failure. CNC machining removes that risk.
Which tasks benefit from CNC over manual processes?
Manual machining still has a place in custom, one-off jobs. But when speed, precision, or volume is required, CNC is the better choice.
Tasks that require high precision, repetition, or complex geometries benefit most from CNC machining over manual processes.

Complex shapes and contours
CNC machines excel at producing intricate shapes, deep cavities, and internal channels. These are nearly impossible to do consistently by hand.
Repetitive batch production
For components needed in large volumes, CNC shines. Once a program is loaded and tested, machines can repeat the task for thousands of parts with no variation.
Prototyping and fast iteration
CNC is ideal for making quick prototypes, especially when time to market matters. Programs can be adjusted rapidly, allowing designers to tweak geometry without resetting a whole manual process.
Use cases where CNC wins
Here are examples of specific applications:
| Task | Preferred Method | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Gear production | CNC | Precision & batch consistency |
| Custom one-off fixture | Manual | Low volume, flexibility |
| High-volume aluminum housing | CNC | Speed and uniformity |
| Deep cavity mold component | CNC | 3D contours and toolpath control |
| Prototype of plastic part | CNC | Fast iteration & detail |
CNC makes sense where deadlines are tight, designs are complex, or customers demand consistency.
Where is CNC machining preferred over manual processes?
Some industries can’t afford to rely on trial-and-error. They need dependable, repeatable quality in every component.
CNC machining is preferred in aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics industries where precision and repeatability are critical.
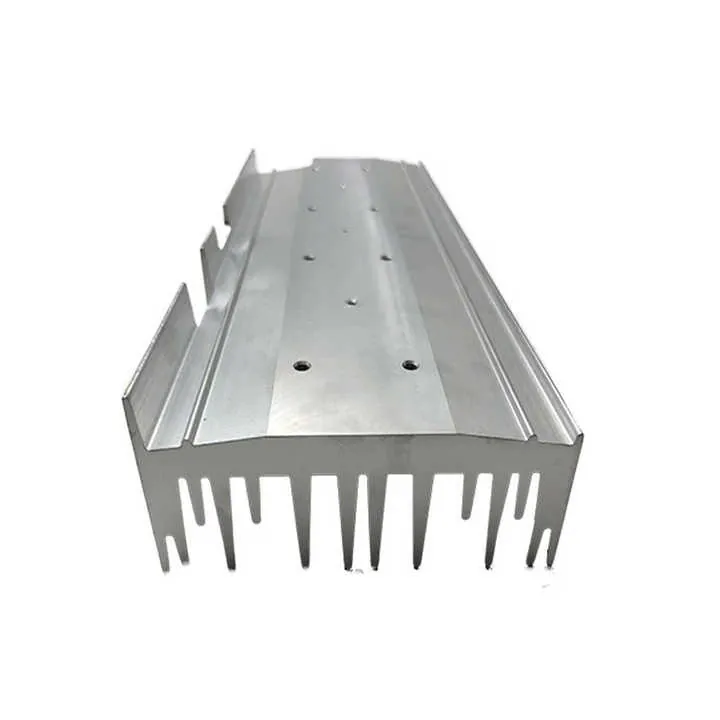

Aerospace and defense
Aircraft components demand tight tolerances and traceability. CNC machines not only meet these specs but also generate digital logs and inspection data.
Medical devices
Surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic components require microscopic precision. CNC ensures no contamination or deviation from approved designs.
Automotive and EV parts
From engine components to aluminum housings for EV batteries, CNC ensures every part fits perfectly and performs reliably.
Electronics and semiconductors
CNC is essential for fabricating heat sinks, PC housings, and high-performance thermal modules. Manual methods can't match the geometric precision required.
Industry comparison
| Industry | CNC Use Cases | Manual Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Brackets, ducts, engine parts | Inconsistent precision |
| Medical | Bone plates, surgical tools | Risk of contamination |
| Automotive | Housings, frames, mounts | Slow production rate |
| Semiconductor | Heat sinks, PC structures | Cannot meet tight tolerances |
In these industries, errors cost lives or millions in rework. CNC gives manufacturers confidence in the parts they deliver.
Conclusion
CNC machining provides better speed, precision, and repeatability compared to manual methods. It's the go-to choice for industries where consistency and accuracy are non-negotiable.






