Aluminum is lightweight, strong, and easy to shape. Combine that with CNC machining, and you get one of the most efficient ways to make modern parts.
CNC aluminum refers to aluminum components that are manufactured using computer-controlled machines, offering high precision, repeatability, and clean finishes in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
It’s no surprise that aluminum is one of the most popular materials in CNC shops. It cuts fast, cools quickly, and finishes beautifully. Let’s see how CNC and aluminum work together.
How does CNC machining work for aluminum?
Aluminum may be easier to cut than steel, but it still needs the right process to get the best results. CNC makes it possible.
CNC machining works on aluminum by using computer-guided tools to cut, drill, or mill the material with extreme precision, removing layers to create the final shape.

The process begins with a digital design, usually made in CAD software. That model is converted into G-code, which tells the CNC machine exactly how to move.
Once the aluminum block or sheet is loaded, the CNC machine runs the code—moving tools along multiple axes (usually 3, 4, or 5) to perform cutting, drilling, tapping, and contouring.
CNC Machining Steps for Aluminum:
- Design – Use CAD to create a model
- Programming – Generate G-code using CAM software
- Setup – Load aluminum stock and secure it
- Toolpath Execution – CNC cuts the material in sequence
- Finishing – Deburring, anodizing, polishing, or coating
Aluminum Machining Capabilities:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| CNC Milling | Complex shapes, pockets, contours |
| CNC Turning | Cylindrical or round parts |
| Drilling/Tapping | Accurate holes, threaded sections |
| Surface Finishing | Smooth surfaces, ready for coating |
| Engraving | Logos, part numbers, labels |
Because aluminum dissipates heat quickly, it allows faster tool speeds and shorter cycle times. That makes production both fast and cost-effective.
Why is aluminum commonly machined with CNC?
There are many materials to choose from—but aluminum wins for speed, flexibility, and cost. That’s why it’s a favorite in CNC shops.
Aluminum is commonly machined with CNC because it is soft, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, easy to cut, and supports tight tolerances while offering excellent surface finishes.

Compared to harder metals like steel or titanium, aluminum machines more easily. This leads to less tool wear, lower cutting forces, and cleaner chips.
Key Benefits of CNC Machining Aluminum:
| Benefit | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| High Machinability | Cuts faster and with less tool pressure |
| Good Thermal Conductivity | Cools quickly during cutting |
| Lightweight | Ideal for weight-sensitive applications |
| Strong Enough | Balances strength and low density |
| Corrosion-Resistant | Lasts longer in harsh environments |
| Recyclable | Eco-friendly and cost-efficient |
It also supports many surface finishes:
- Anodizing – Adds corrosion resistance and color
- Powder Coating – Tough, decorative finish
- Polishing – Smooth, reflective surfaces
- Bead Blasting – Matte, uniform texture
These options make aluminum suitable for parts that are both functional and visible—like consumer electronics or vehicle components.
Which CNC tools are used for aluminum?
To cut aluminum properly, you need the right tools. Dull or incorrect tooling can cause chatter, poor finish, or even tool breakage.
CNC aluminum machining uses specialized tools such as carbide end mills, high-speed steel cutters, and coated inserts designed to stay sharp and remove material efficiently.
Aluminum is soft—but it tends to stick to tools due to its low melting point. So, tools need sharp edges, large flutes, and often a coating to prevent buildup.
Common Tools for Aluminum CNC Work:
| Tool Type | Usage |
|---|---|
| Carbide End Mills | High-speed, clean cuts, long tool life |
| HSS End Mills | Cost-effective for short runs |
| Single Flute Cutters | Good for plastics and thin aluminum sheets |
| Drill Bits | Precision holes with tight tolerances |
| Taps & Thread Mills | Creating threads in soft aluminum |
| Fly Cutters | Flat finishes on large surface areas |
Tool Coatings That Help:
| Coating Type | Benefit for Aluminum |
|---|---|
| ZrN (Zirconium Nitride) | Reduces sticking and improves chip flow |
| TiB₂ (Titanium Diboride) | Resists aluminum adhesion and keeps tools cool |
| DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) | Boosts wear resistance and smooth cutting |
Tooling Tips:
- Use high spindle speeds (10,000+ RPM)
- Use large chip loads to avoid melting
- Apply compressed air or coolant to clear chips
- Keep tools sharp—dull tools lead to bad finishes
With the right tooling and parameters, aluminum can be cut as smoothly as butter—producing sharp edges, accurate dimensions, and polished surfaces.
Where is CNC aluminum machining applied?
Because it’s strong yet light, aluminum is used in everything from rockets to smartphones. And CNC machining makes it all possible.
CNC aluminum machining is widely applied in aerospace, automotive, electronics, robotics, medical devices, and consumer goods where precision and lightweight parts are critical.
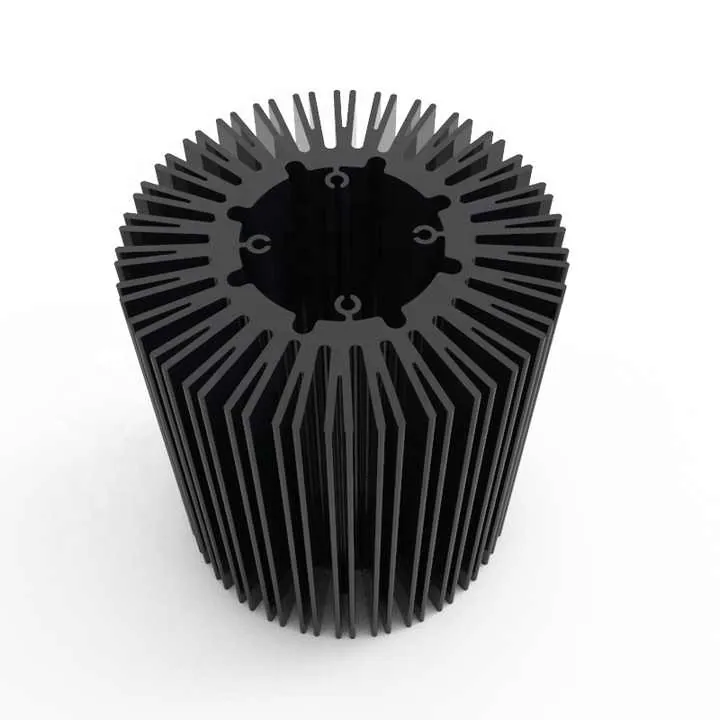

Its versatility makes aluminum a perfect match for CNC. Whether you're making one prototype or 10,000 parts, it performs reliably.
Industry Applications:
| Industry | CNC Aluminum Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Structural parts, brackets, avionics housings |
| Automotive | Engine parts, wheels, transmission casings |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, casings, connectors |
| Medical | Surgical tools, housings, mounts |
| Robotics | Lightweight arms, joints, brackets |
| Consumer Products | Laptop frames, camera parts, custom enclosures |
Real-World Examples:
- A drone frame made from CNC-milled 7075 aluminum for weight reduction
- Anodized aluminum laptop shell that looks clean and stays cool
- LED light housings designed with fins for heat dissipation
- Aluminum molds for plastic part injection—fast and cost-effective
With tight tolerances, great surface options, and low weight, aluminum is the preferred metal for high-performance parts—and CNC machining is the best way to shape it.
Conclusion
CNC aluminum is a smart solution for strong, lightweight, and precise components. It combines the versatility of aluminum with the accuracy of CNC machining, making it essential in industries that demand efficiency, speed, and quality.






