CNC cutting can feel like a complex industrial process. Many people hear about it but don't know how it really works or what makes it special.
CNC cutting is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed software to guide machines in cutting, drilling, or milling materials with high precision.
Understanding how CNC cutting works and where it is used can help you make better decisions, whether you're sourcing parts or looking for better production methods.
How does CNC cutting work?
CNC sounds high-tech and confusing. If you’ve ever seen a big metal machine slicing through solid materials like it’s butter, you’ve seen CNC in action—but what actually drives it?
CNC cutting works by using digital software to control tools that cut or shape materials with extreme accuracy.

CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. At the core of the process is a computer program. This program tells the machine what to do, when to move, how deep to cut, and where to stop. The instructions come from CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files, which are converted into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) instructions.
Once the instructions are ready, the CNC machine follows the code to move tools like blades, drills, or mills. These tools operate on different axes—X, Y, and Z. Some advanced machines also rotate in multiple directions (4-axis or 5-axis), allowing them to cut complex shapes.
Steps of the CNC Cutting Process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| CAD Design | A digital design is created with 2D or 3D modeling software. |
| CAM Processing | The design is converted into machine-readable code (G-code). |
| Machine Setup | Operators set up tools, position material, and secure clamps. |
| Cutting Process | The machine executes the code, cutting the material as needed. |
| Inspection | Finished parts are measured to ensure quality and precision. |
The whole process is automated once it begins. It doesn’t need constant human supervision. The result is high consistency, speed, and accuracy. It also reduces material waste because the cuts are clean and efficient.
Why choose CNC cutting for precision?
Precision matters. A small error in cutting could lead to large failures in product performance. Traditional cutting methods often depend on manual skill. But human hands can't match the steadiness of machines.
CNC cutting delivers unmatched accuracy, consistent quality, and the ability to replicate complex designs with minimal error.

CNC cutting has become the go-to method for industries that require extreme precision, like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. These sectors cannot afford mistakes. A hole that is 0.2 mm off may cause the entire part to fail. CNC solves this.
Key Benefits of CNC Cutting for Precision
- Tight Tolerances: CNC machines can achieve tolerances as close as ±0.01 mm.
- Repeatability: You can produce thousands of identical parts with no variation.
- Less Material Waste: Every cut is planned, reducing offcuts and scrap.
- Speed: What takes hours manually, CNC can do in minutes.
- Complex Geometry: It handles intricate and 3D shapes easily.
When you’re making parts that must fit perfectly, CNC cutting reduces the chances of errors caused by fatigue, misjudgment, or tool wear. The machine keeps performing the same task without getting tired.
Real-World Example
A German medical tool manufacturer needed titanium components cut to exact specs. Using CNC, they achieved precision with less than 0.01 mm deviation—something human hands could not replicate. It reduced their rework rate by 95%.
Which materials are ideal for CNC cutting?
Not all materials behave the same when cut. Some are soft, others brittle, and some are extremely hard. So how do we know what works well for CNC cutting?
CNC cutting is suitable for a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, woods, and composites.

Most Common Materials Used in CNC Cutting
| Material Type | Examples | Notes on Use |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Aluminum, Steel, Brass | Ideal for structural and mechanical components. |
| Plastics | Acrylic, Nylon, ABS | Good for light-duty parts, cases, or prototypes. |
| Wood | Plywood, MDF, Hardwood | Used for furniture, models, or packaging molds. |
| Composites | Carbon Fiber, G10 | Lightweight and strong, often used in aerospace and racing. |
Why Aluminum is a Favorite
Aluminum, especially grades like 6061-T6 and 7075, is often preferred because it’s easy to machine and very strong. It’s used widely in industries that demand both light weight and strength.
Features That Make a Material CNC-Friendly
- Machinability: How easily the material can be cut.
- Heat Resistance: Materials that don’t deform easily during cutting.
- Strength vs. Weight: Especially important for automotive and aerospace parts.
- Cost: Raw material and tool wear costs vary by material.
Each material has its own settings for speed, tool type, and depth. The right combination helps avoid tool breakage or poor finish.
Where is CNC cutting applied?
CNC cutting sounds like something only big factories use. But it's everywhere—from cars to laptops, and even in your kitchen.
CNC cutting is widely applied in industries like aerospace, automotive, construction, electronics, and custom manufacturing.
The versatility of CNC technology allows it to serve a wide range of industries. It’s used not just for metal parts but also for custom signage, wood panels, plastic enclosures, and more.
Common Industries That Use CNC Cutting
- Aerospace: Components like brackets, engine parts, and housings.
- Automotive: Chassis parts, engine components, and custom tuning parts.
- Construction: Aluminum frames, brackets, and moldings for facades.
- Furniture & Interiors: Custom wooden panels, plastic covers, or fittings.
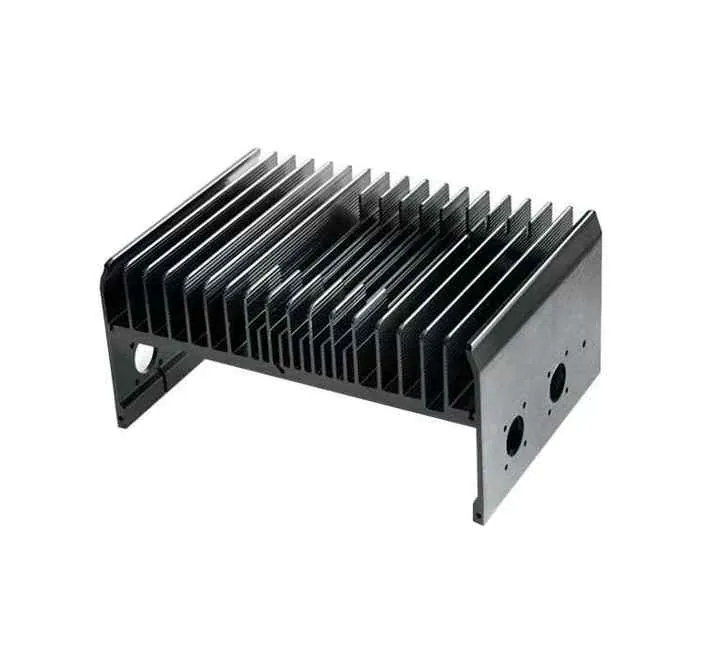
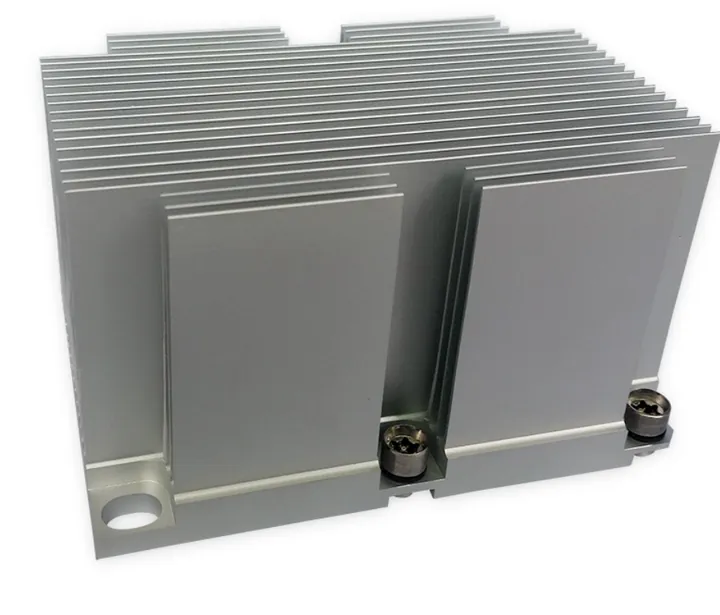
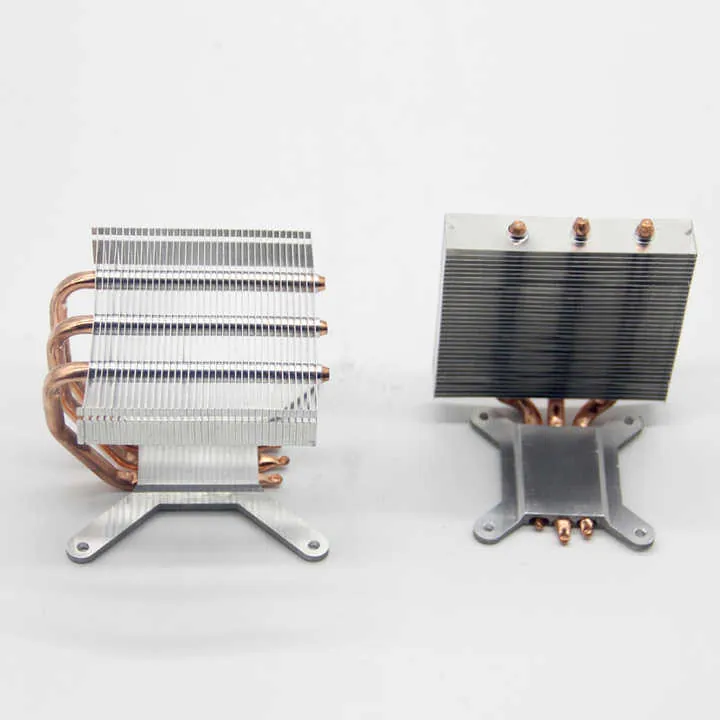
- Electronics: Housings, panels, and heat sinks.
Specialty Applications
Even art and design studios use CNC to create complex sculptures and installations. Small business owners use it to make personalized gifts, and tech startups use CNC to build prototypes quickly.
CNC in the Solar Industry
At Sinoextrud, many of our clients in the solar panel business use CNC cutting for aluminum frame systems. These frames must be precise to hold glass panels safely and fit into larger structures.
CNC cutting ensures the holes and lengths are exactly right—saving installation time and reducing onsite errors.
Conclusion
CNC cutting is more than just a manufacturing trend. It’s a precision-driven, highly adaptable technology that shapes modern industry. From metal to wood, from car parts to clean energy—CNC keeps things sharp and consistent.





