CNC has transformed how products are made. It lets machines follow digital instructions to shape parts with great accuracy. This leads to fewer errors and faster production.
CNC in manufacturing means using computer-controlled machines to produce parts. It improves accuracy, saves time, and ensures consistent quality in high-volume or high-precision production.
CNC is not just a tool. It's a method that helps factories make complex parts faster, with fewer mistakes. Knowing how CNC works shows why it's widely used across industries.
How does CNC improve manufacturing?
Before CNC, many tasks were done by hand. Workers used manual tools and measured by eye. That caused slow production and more errors. CNC replaces that with automated steps and exact control.
CNC improves manufacturing by automating production steps, increasing precision, reducing waste, and enabling faster turnaround of high-quality parts.

CNC machines follow instructions without getting tired or making mistakes. They can run 24 hours a day. They produce parts that match exactly, even after thousands of runs.
Key improvements CNC brings to manufacturing
1. Automation
CNC machines don’t need constant human control. Once the program is set, they work on their own. This saves labor and allows longer work hours.
2. Precision
CNC machines can make very small cuts, often within 0.01mm. That kind of accuracy is hard to achieve by hand.
3. Speed
Manual production takes more time per piece. CNC machines move quickly and cut faster, which shortens production time.
4. Less waste
Because CNC follows the exact path, it reduces mistakes. Less scrap means less material cost.
5. Better quality
CNC machines produce parts with smooth surfaces and correct sizes. You don’t need to rework as much.
Summary of benefits
| Improvement | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation | Reduces manual work and speeds up processes |
| Precision | Delivers tight tolerances consistently |
| Speed | Cuts and shapes material faster |
| Waste reduction | Minimizes scrap from human errors |
| Surface quality | Often needs no secondary finishing |
These improvements help manufacturers stay competitive. CNC allows more products to be made faster, cheaper, and with better quality.
Why use CNC in manufacturing processes?
Factories use CNC not just for speed, but for control. Manual methods leave room for error. CNC cuts that risk. It allows you to plan, test, and then run a job without surprise.
CNC is used in manufacturing because it ensures accuracy, supports complex part production, lowers labor costs, and delivers consistent results across batches.
CNC takes the guesswork out of machining. With a well-written code, the outcome is known even before the first cut. That kind of control lets manufacturers plan better and reduce delays.
Why manufacturers rely on CNC
Reliability in production
Once programmed, the machine does exactly the same task every time. This is important when every part must match.
Labor savings
With CNC, fewer workers can oversee more machines. That cuts labor costs without hurting output.
Handling complex tasks
Some cuts and shapes are impossible or too slow by hand. CNC machines do them with ease, including curves, slots, and angles.
Easy adjustments
Changing a CNC job is as easy as updating a file. This makes it flexible and fast to respond to changes.
Integrated with design
CAD models can be directly turned into parts. That means fewer steps and errors between design and production.
Real-world example
In one project, I needed to produce 300 custom brackets for a client. With CNC, once I finished the code and ran one test, I made all 300 in 2 days. Each one matched perfectly. No extra inspection or rework was needed.
Which tasks benefit from CNC in manufacturing?
Not all tasks need CNC. But in high-precision jobs, or when repeatability matters, CNC has a clear edge. These tasks gain better quality and lower cost.
Tasks that benefit include high-volume production, precision machining, complex parts, and custom one-off components.
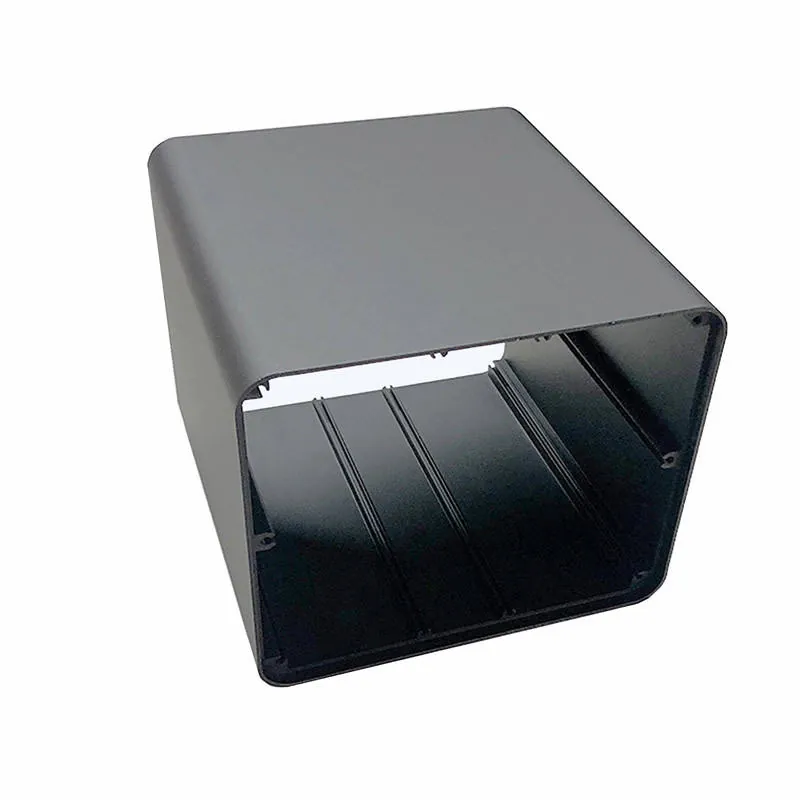

Here are common manufacturing tasks made better with CNC:
High-volume production
When you need thousands of parts, CNC ensures they all come out the same. This reduces inspection time and ensures product quality.
High-tolerance machining
Some parts must fit tightly with others. CNC achieves the tight tolerances needed for gears, engine parts, and structural components.
Custom parts
Each job may need different sizes or features. CNC can change quickly between tasks just by loading a new file.
Rapid prototyping
For new designs, CNC can quickly produce a first version. This helps teams test and improve their product.
Tasks improved by CNC
| Task type | CNC Advantage |
|---|---|
| Mass production | Repeatable and fast |
| Complex geometry | Handles curves, angles, and holes with ease |
| One-off custom jobs | Fast code change and flexible setup |
| Prototyping | Quick turnaround for early product testing |
| Tight tolerance parts | Reliable dimensions every time |
Multiple industries benefit
These tasks show up across industries. From car parts to medical tools, from furniture to machine housings, CNC helps each step run better.
Where is CNC widely used in manufacturing?
CNC is not limited to metal or machines. It's used across many industries. Wherever accurate, repeatable parts are needed, CNC plays a key role.
CNC is widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical, and even furniture and architecture manufacturing.
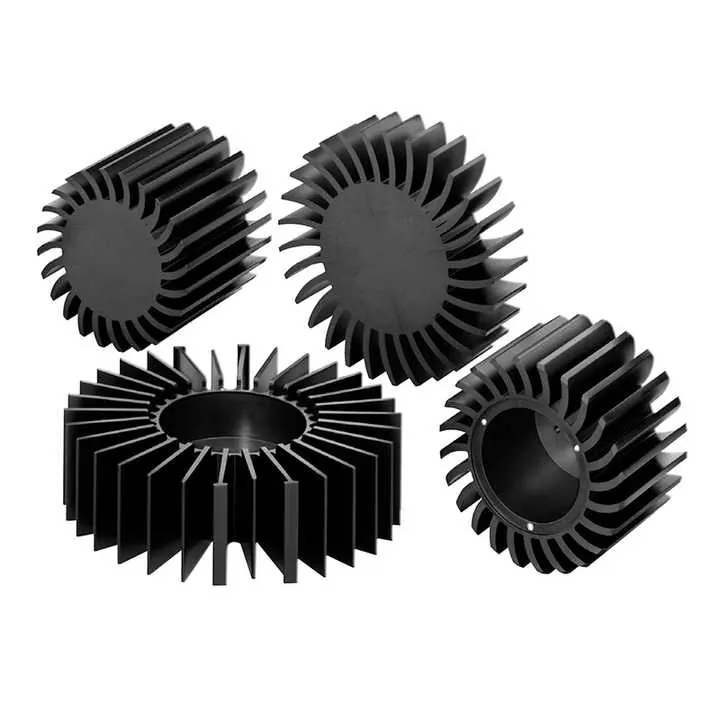

Here are major industries and how they use CNC:
Automotive
Parts like gears, engine blocks, and brackets are made by CNC. These parts must match designs exactly.
Aerospace
Aircraft need very high standards. CNC makes lightweight, strong, and accurate parts from aluminum and titanium.
Medical
Implants, surgical tools, and equipment cases require precision. CNC helps meet health standards.
Electronics
CNC machines cut cases, panels, and plastic frames for devices. It also carves tiny parts for circuit boards.
Furniture and architecture
Wood CNC machines shape furniture parts, doors, and décor with exact dimensions.
Examples by industry
| Industry | CNC Application Examples |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine parts, custom brackets, gear systems |
| Aerospace | Wing components, engine housings, panels |
| Medical | Bone plates, surgical tools, device enclosures |
| Electronics | Plastic housings, heat sinks, brackets |
| Furniture | Custom wood panels, carved edges, designs |
Global trend
In recent years, even small factories around the world started using CNC. It’s now part of both mass production and custom one-off jobs. In China, CNC is now a core process in aluminum extrusion finishing. It turns rough profiles into exact components.
Conclusion
CNC is a key tool in modern manufacturing. It cuts, shapes, and finishes parts based on digital designs. By improving accuracy, speed, and flexibility, CNC helps factories deliver better products in less time.






