Sometimes, traditional cutting tools or manual machines can't meet modern precision needs. This creates delays, waste, and higher costs.
CNC machining is a digital manufacturing process that uses computers to control tools for cutting, drilling, and shaping parts from metal or plastic.
Many industries now rely on CNC for its accuracy, speed, and repeatability. In this article, I’ll break down how CNC works, its benefits, which parts need it, and where it's used.
How does CNC machining work?
Manual machining often depends on human skill. This can lead to errors or inconsistent parts. It's also time-consuming and lacks efficiency in complex designs.
CNC machining works by converting digital designs into instructions (G-code), which guide automated tools to cut or shape material with high precision.
At its core, CNC stands for “Computer Numerical Control.” This means a computer runs the machine using a pre-programmed code. The operator loads the digital design, usually from CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design is then translated into G-code using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
The CNC Process Step-by-Step
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Design | A CAD file is created to define the shape and size of the part |
| 2. Programming | CAM software turns the design into machine instructions (G-code) |
| 3. Setup | Material is fixed onto the CNC machine bed |
| 4. Machining | The CNC machine follows the code and shapes the part |
| 5. Inspection | The finished part is checked for accuracy and surface finish |
CNC Machines and Tools
There are many types of CNC machines:
- CNC mills for cutting complex shapes
- CNC lathes for turning cylindrical parts
- CNC routers for lightweight materials like plastic or wood
- CNC EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) for very hard metals
- CNC plasma and laser cutters for cutting through metal sheets
In aluminum extrusion, the most common CNC machines are vertical CNC mills, which allow for drilling holes, making cutouts, and even 3D profiling of complex parts.
CNC machines move along axes—usually three (X, Y, and Z), but some advanced systems use five or more. These axes allow the cutting tools to approach the material from multiple angles, which is useful for parts with undercuts or complex surfaces.
The biggest advantage is the accuracy. Most modern CNC machines can hold tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm. That level of precision is hard to achieve with manual tools.
Why use CNC for production?
Manual tools are slow and require skilled workers for each part. This makes scaling production expensive and risky. Mistakes can cost time and materials.
CNC offers repeatable precision, speed, and flexibility, making it ideal for medium to large-scale production across industries.
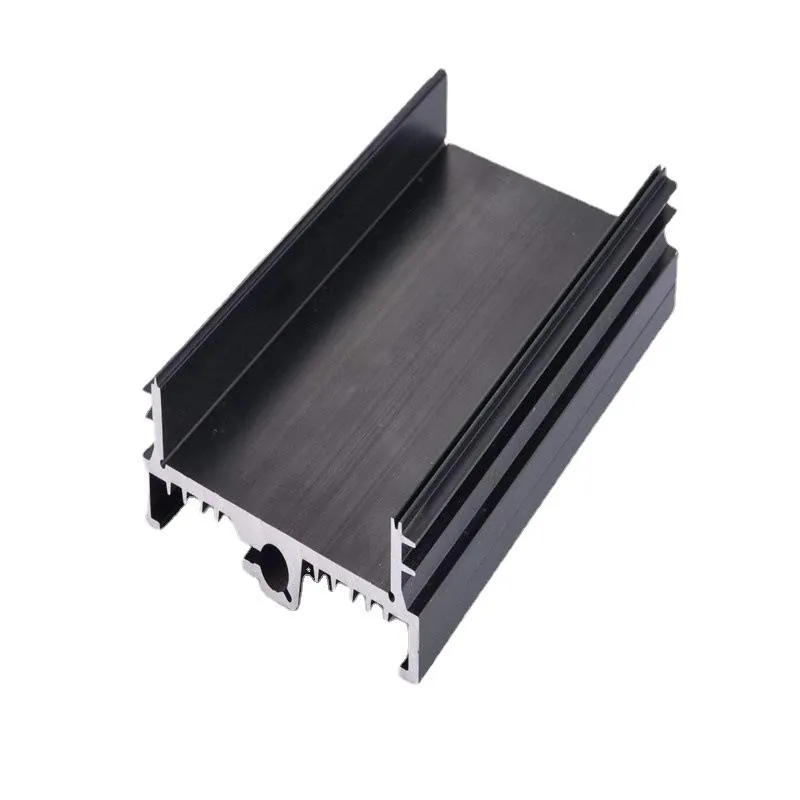

CNC machines are used in both prototyping and full-scale production. Because the process is digital, switching from one design to another takes minutes. You don’t need to retool or retrain operators.
Key Benefits of CNC Machining in Production
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Precision | Maintains tight tolerances even in complex designs |
| Speed | Automated tools reduce production time significantly |
| Repeatability | Every part comes out exactly the same, batch after batch |
| Flexibility | Easily switch between designs or parts |
| Lower Labor Cost | Fewer skilled operators are needed |
| Quality | Smooth finishes and clean edges, even on difficult materials |
When CNC Makes the Most Sense
In my experience with custom aluminum profiles, CNC is most helpful when:
- The customer needs tight tolerances.
- The design includes complex shapes or multiple drill holes.
- Surface finish is important, especially for consumer products.
- The order quantity is between 10 to 10,000 pieces.
- The project includes prototypes, but may scale to mass production later.
For example, we often machine solar panel aluminum frames with custom mounting slots. These would be hard to produce by extrusion alone, and impossible to do manually at scale. CNC makes these features precise, fast, and affordable.
Which parts need CNC machining?
Not all aluminum profiles need CNC. Simple lengths can be cut and shipped without further work. But some shapes are too complex for extrusion or cutting alone.
Parts that require tight fits, special shapes, or post-processing often rely on CNC to meet functional or design needs.
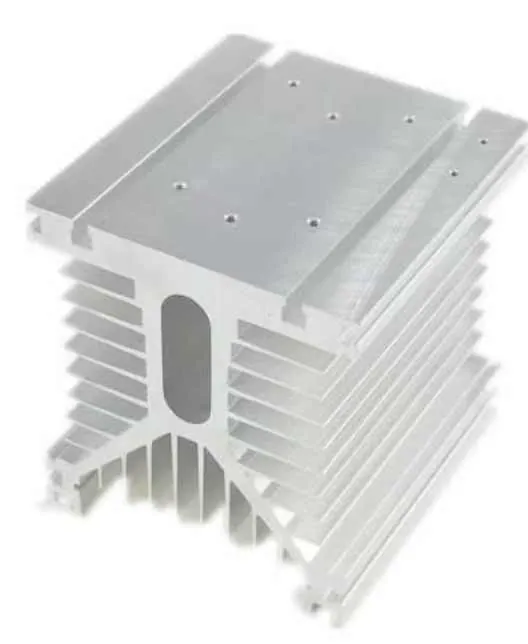

Common CNC-Machined Parts from Aluminum Extrusions
| Part Type | Reason for CNC Machining |
|---|---|
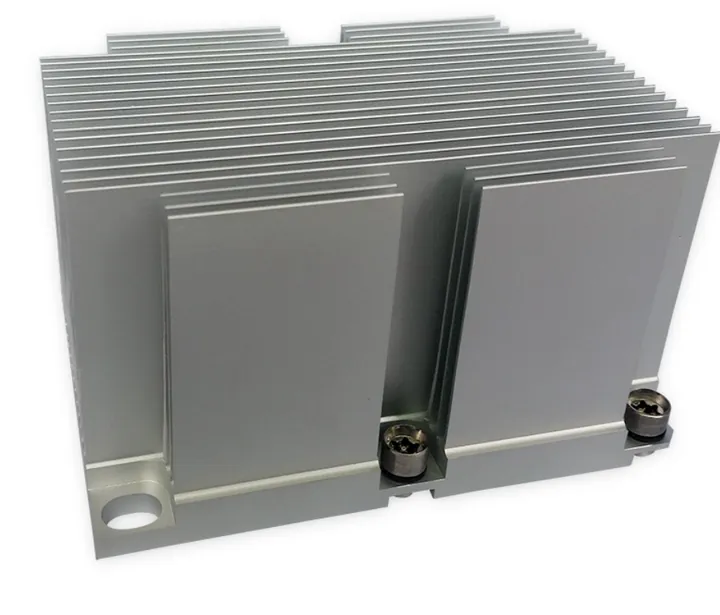
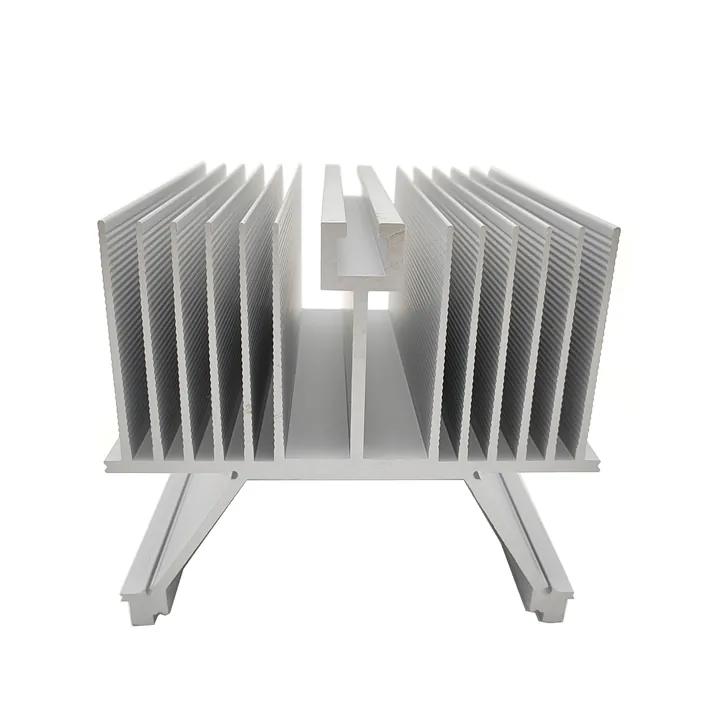
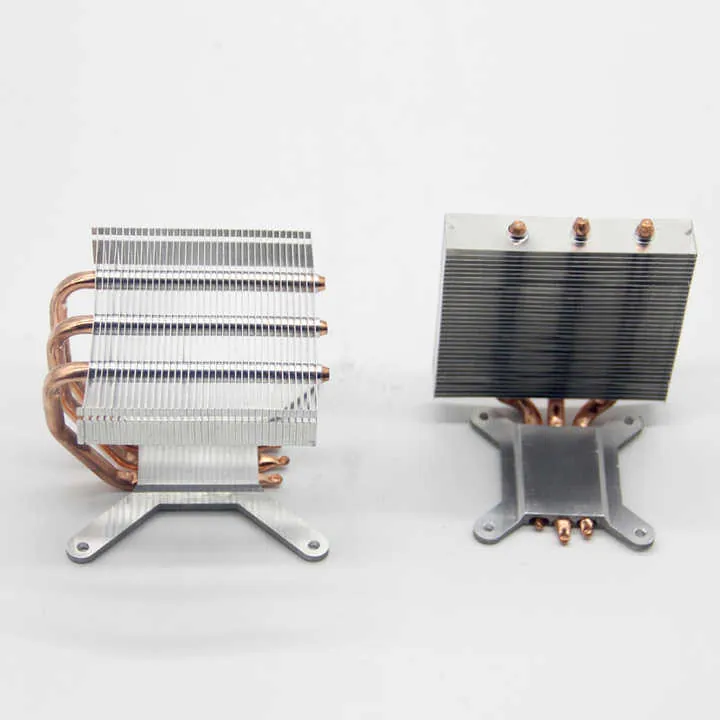
| Heat sinks | Fine fin spacing, flat base for heat contact |
| LED housings | Precision cutouts for circuit boards |
| Mounting brackets | Accurate hole positions and tight fit |
| Solar panel frames | Custom slots and holes for mounting |
| Furniture connectors | Smooth joints, hidden screws |
| Electronic enclosures | Ports, ventilation, assembly features |
When CNC Adds Value
Let’s say a customer needs an extrusion for a sliding window frame. The basic profile is simple. But the handle hole, drainage slots, and screw channels need to be placed precisely. If these are off by even 0.5 mm, the parts may not fit or leak.
That’s where CNC comes in. It ensures:
- All holes are aligned.
- Slot depth is consistent.
- Tolerances are controlled within limits.
Also, surface finish matters. CNC-machined parts have cleaner edges. We can even do deburring, chamfering, or threading in one setup.
Many parts are used in visible areas, like architecture or electronics. A clean, professional finish makes a big difference. CNC lets us deliver that finish at scale.
Where is CNC machining applied?
Many think CNC is only for automotive or aerospace. In fact, it is used in almost every industry where parts must be exact.
CNC machining is used in automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, medical devices, and even renewable energy for producing complex, accurate components.
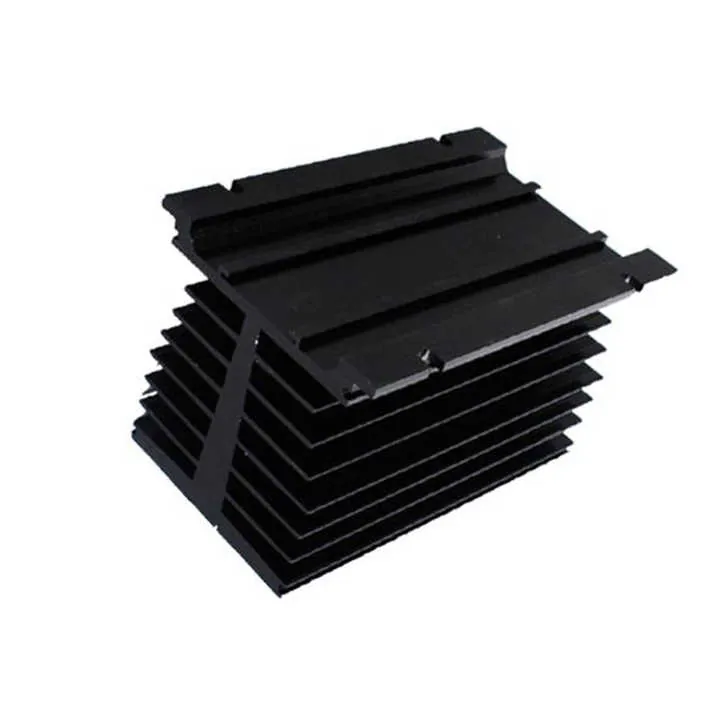

Key Industries Using CNC Machining
1. Automotive
Used for engine parts, brackets, structural frames, and custom tuning parts. CNC allows manufacturers to make thousands of identical parts with zero deviation.
2. Aerospace
Tolerances here are extremely tight. Aluminum alloys are often used due to their light weight. CNC creates components like turbine blades, frames, and housings.
3. Construction
From curtain wall brackets to customized window profiles, CNC adds precision and strength. We’ve worked on many facade systems that require exact alignment.
4. Electronics
CNC machining ensures perfect placement for connectors, ports, and heat dissipation areas. It’s common in server racks, phone casings, and audio equipment.
5. Solar and Renewable Energy
Many mounting systems for solar panels are aluminum-based. CNC is used to make the slot openings, grounding holes, and brackets.
6. Medical Devices
Surgical tools and implants often require high-precision aluminum or titanium parts. CNC delivers repeatable accuracy and clean finishes essential for safety.
My Real-World Experience
We’ve shipped CNC-machined profiles to Germany for an electric vehicle startup. They needed high-quality extruded aluminum parts, machined for battery housing systems. The slots had to match their automated assembly robots. If even one hole was off, the entire production line would stop.
Another client from the Middle East needed architectural fins with special bracket holes. CNC helped us produce thousands of pieces with uniform fit and angle, ready for easy installation on-site.
Conclusion
CNC machining is not just a tool—it's a core part of modern manufacturing. It helps turn custom designs into precise, repeatable parts used across industries. From simple brackets to complex housings, CNC adds speed, accuracy, and value.






